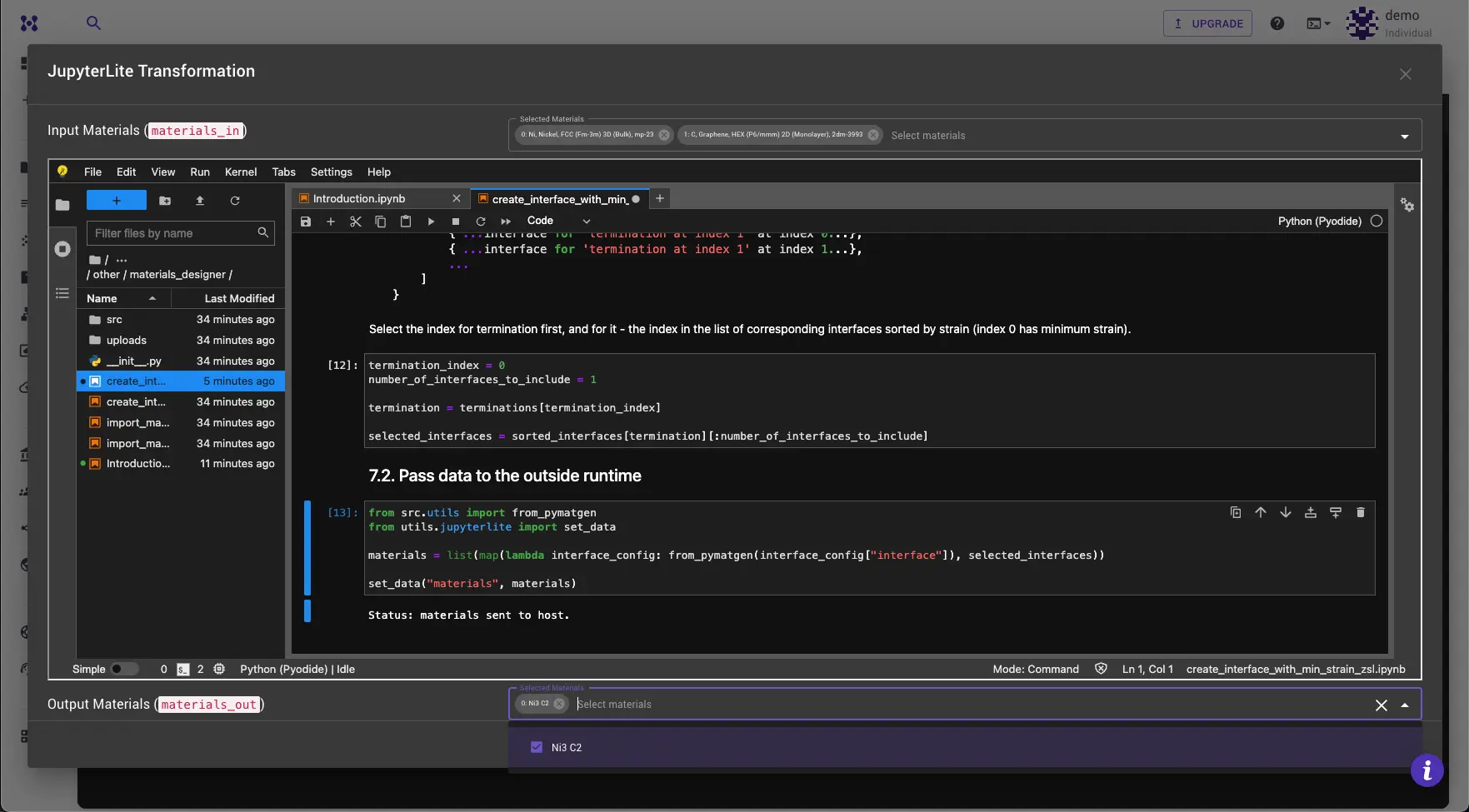
JupyterLite Transformation Dialog¶
The JupyterLite Transformation Dialog enables the modification of materials using Python, Jupyter notebooks with widely used packages (e.g. numpy, pymatgen, ASE, etc.) within the JupyterLite environment, a lightweight implementation of JupyterLab that runs entirely in the web browser.
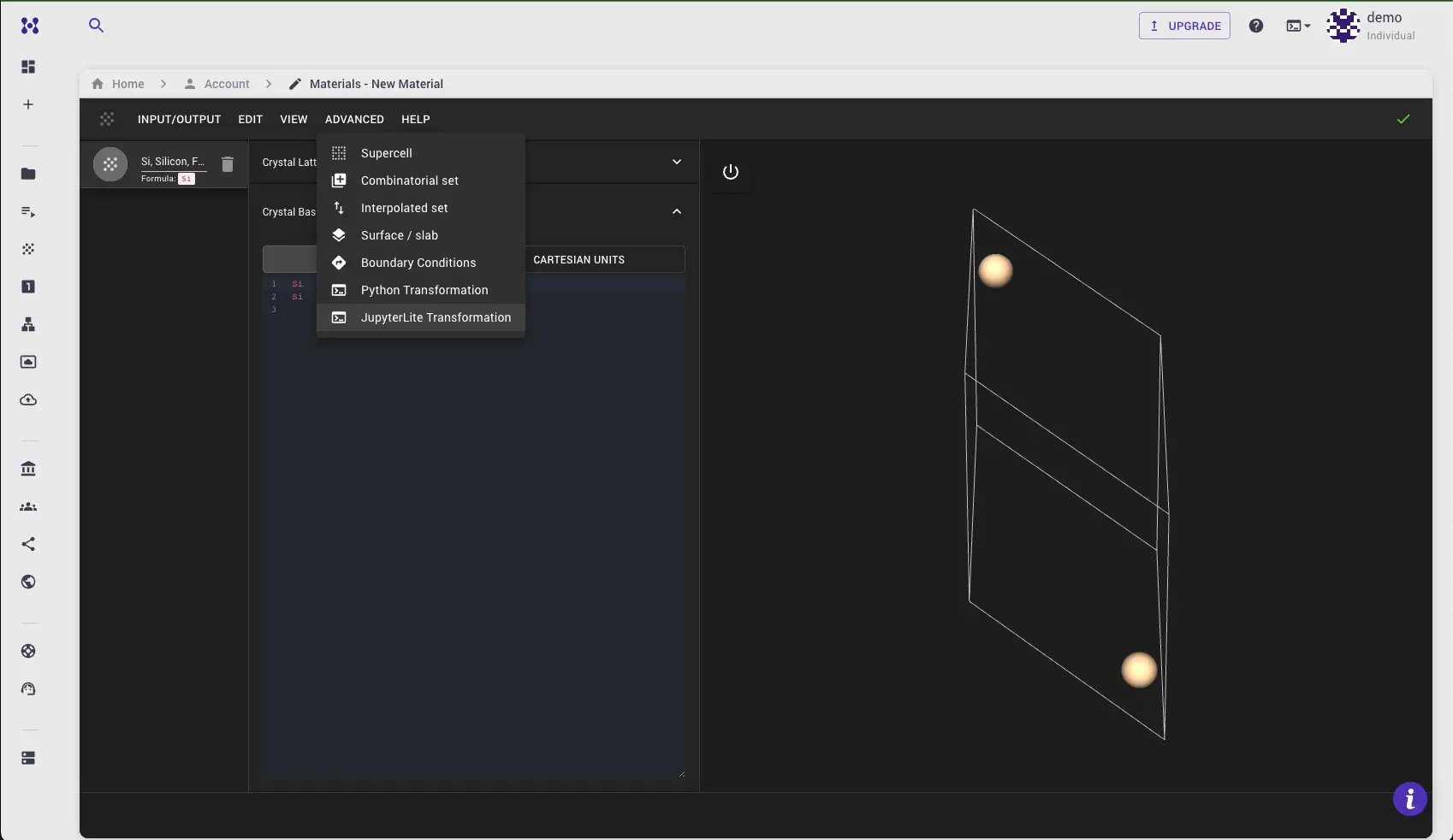
Open Dialog¶
This dialog is accessible via the "Advanced" menu option.
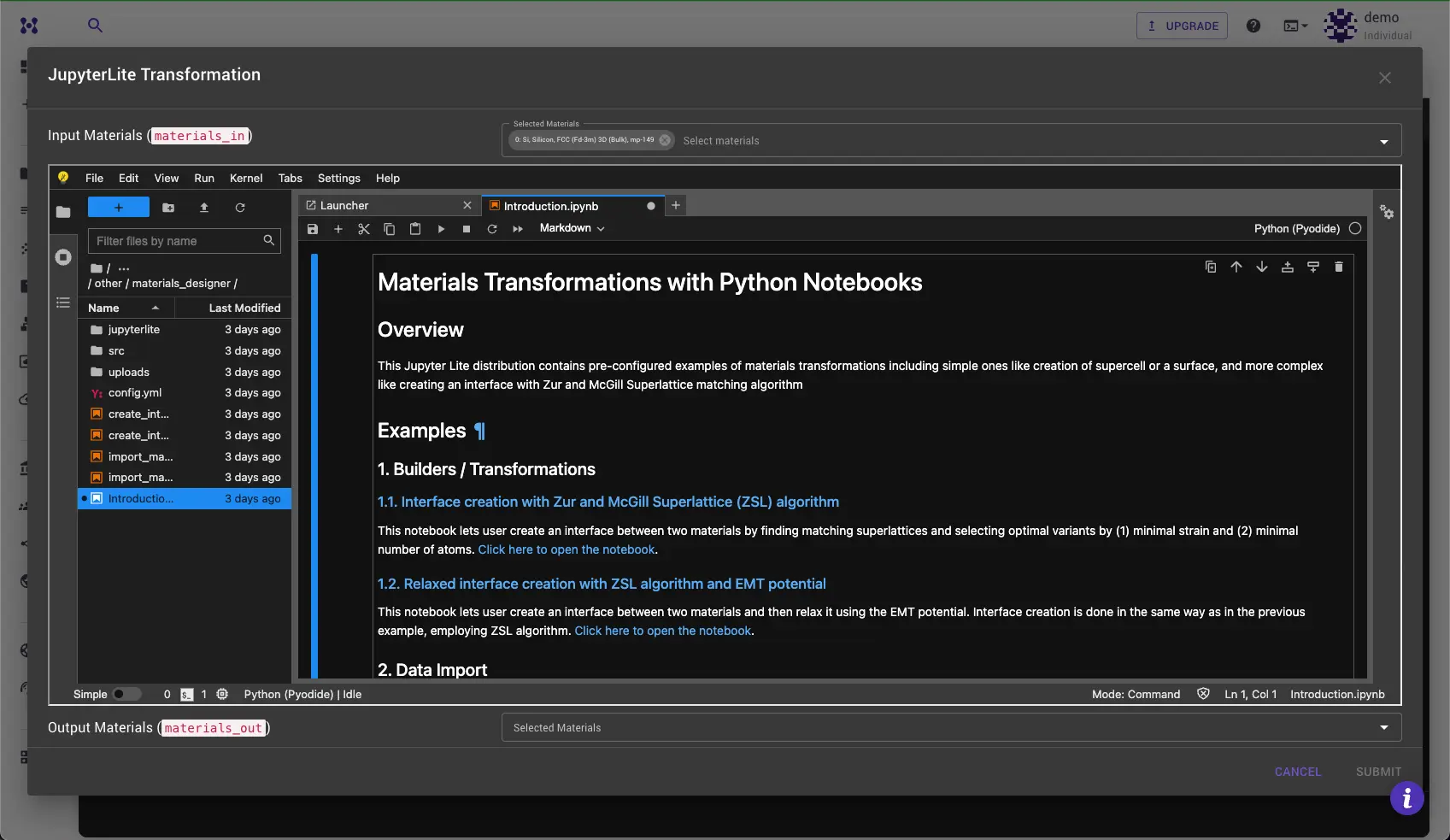
JupyterLite Environment¶
The Dialog facilitates access to JupyterLite Environment where materials from the main application are available.
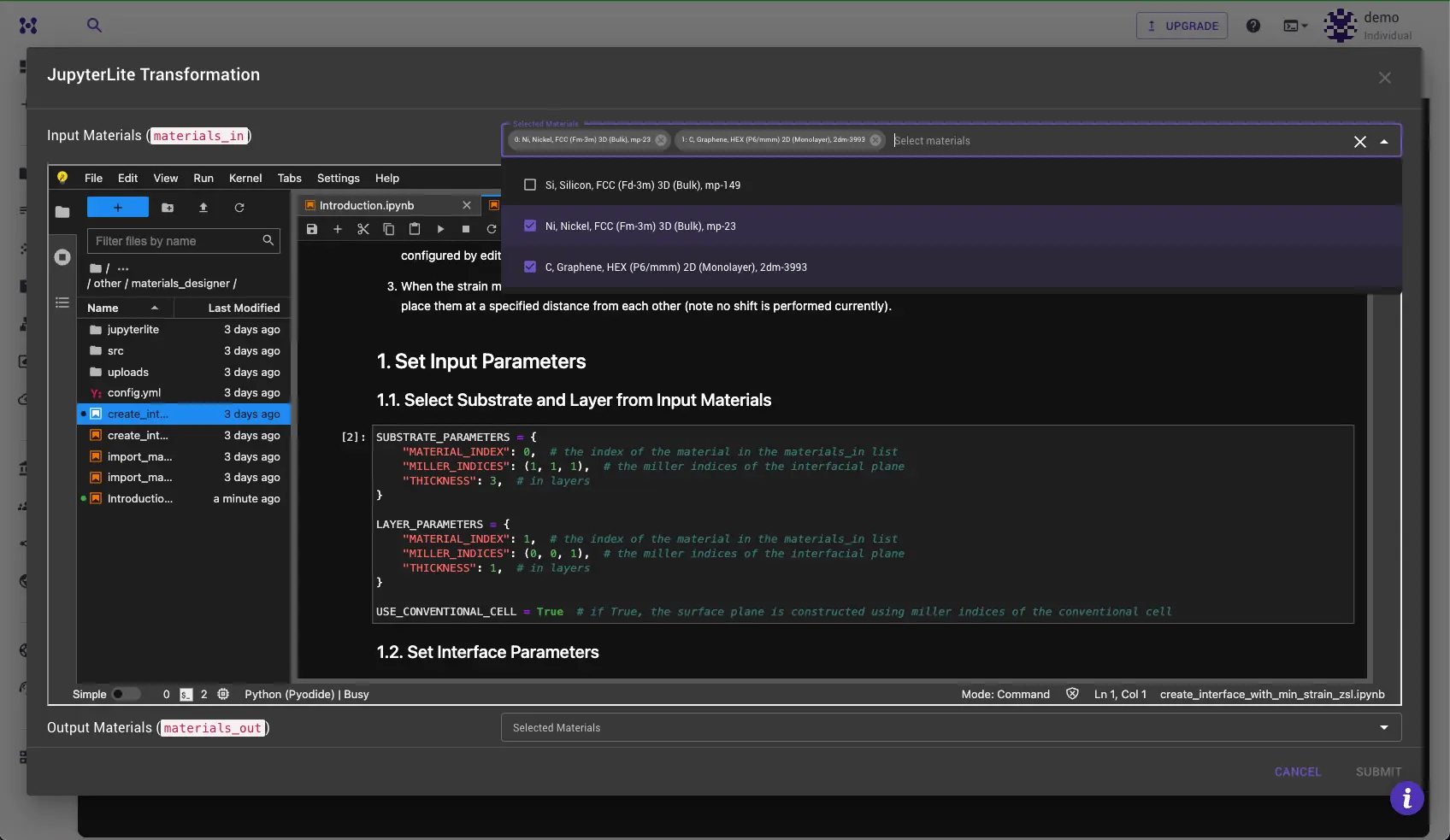
Select Input Materials¶
At the top of the dialog, a drop-down menu allows for the selection of materials to be transferred to the JupyterLite environment. These materials will then be available for further processing within.
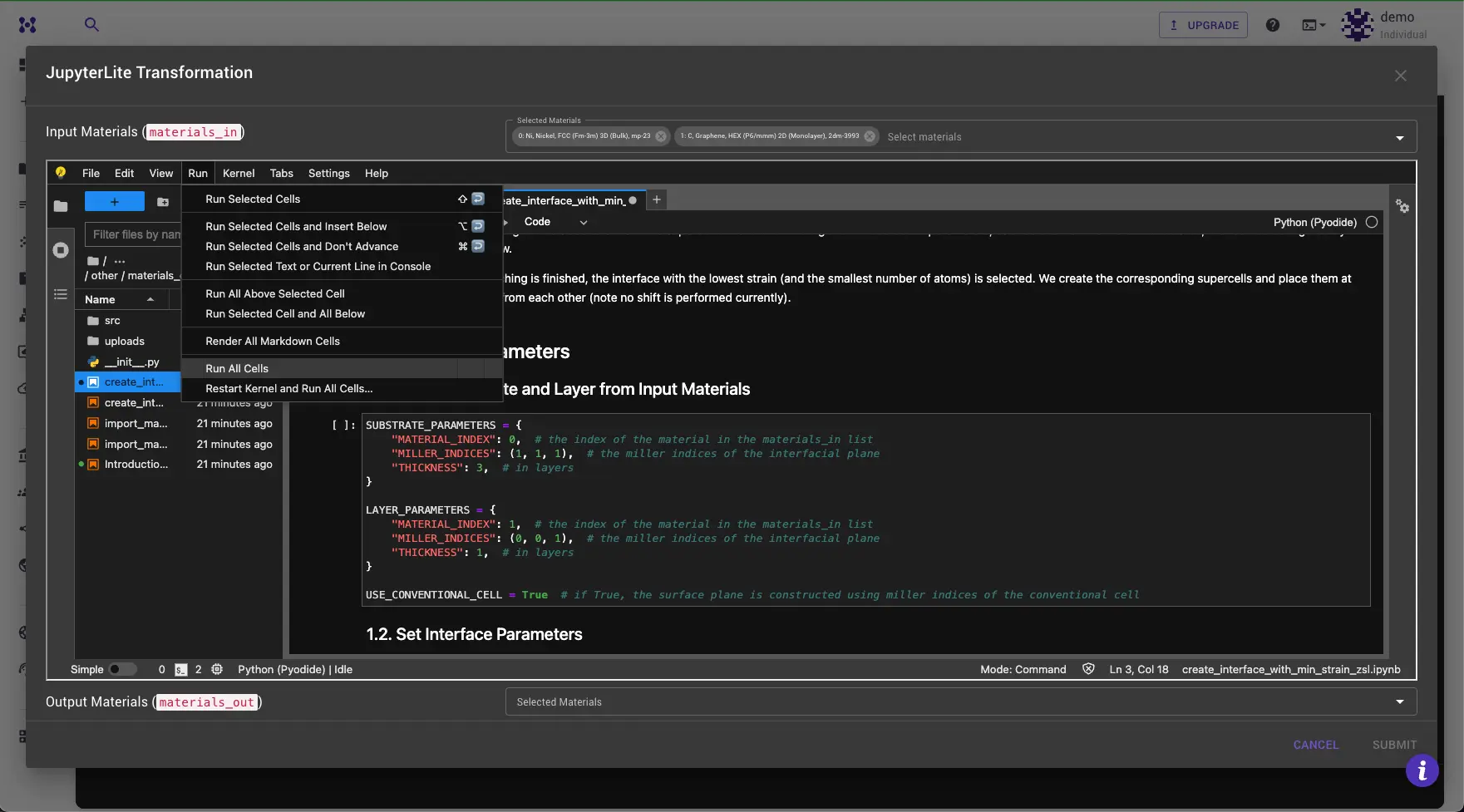
Apply Transformation¶
To apply a transformation, open the notebook containing the desired transformation from the list provided in the Introduction.ipynb notebook. Follow the instructions within to apply the transformation to the selected materials. Typically, this process involves specifying settings for the transformation and clicking "Run All Cells."
Access Materials in JupyterLite¶
To access materials inside the JupyterLite environment, use function from utils.jupyterlite module. The following code snippet demonstrates how to access the materials inside the JupyterLite environment:
1 2 3 | |
Parameters:
The first parameter specifies the name of the global variable ("materials_in") where the received data will be stored.
The second parameter, globals(), ensures that the function operates correctly across both Pyodide and Python environments. It allows get_data to dynamically interact with the global namespace of the script.
Data Handling:
The materials data is initially stored in a global variable named data_from_host, which is updated in response to changes in material selection or the materials themselves.
In the context of the Pyodide environment, data_from_host becomes available after the Pyodide kernel has loaded and the extension set the data.
Send Materials Back to Materials Designer¶
To send the materials back to the Materials Designer, use the following code snippet:
1 2 3 4 | |
Parameters:
The first parameter specifies the data that is being sent, which is "materials" in case for materials, this shouldn't be changed. The second parameter is the list of materials in ESSE format.
Submit Results¶
In most cases the result of the transformation is a set of materials that can be passed back to the Materials Designer. They will appear in the "Materials Out" dropdown at the bottom of the dialog. Select the materials you want to pass back to the Materials Designer and click the "Submit" button to complete the transformation.
Animation¶
The following animation illustrates how to use the JupyterLite Transformation Dialog to create a matching interface between two surfaces using Zur and McGill's algorithm.